
Last week Nvidia released version 451.48 driver update for Windows 10 users. The driver update introduced DirectX 12 Ultimate but also added support for hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling for Windows 10 users running May 2020 Update.
In case you do not know, hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling allows the GPU to manually handle its own memory, removing the operating system from the loop. In theory, this could lead to better performance and will reduce latency. Microsoft added support for hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling in May 2020 Update and the latest driver updates from Nvidia enabled the feature for Nvidia GPUs. If you are using Windows 10 May 2020 Update and have a relatively new Turing based Nvidia GPU, then you can follow the steps below to enable hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling:
- Go to Nvidia’s driver website or use the GeForce Experience app to download and install version 451.48 or later (You can check the current version by opening Nvidia Control Panel)
- Once you have installed the latest drivers, restart your computer
- Click on ‘Search’ on the taskbar and type “Graphics Settings”. Click on the first option to open Windows Graphics settings.
- Click the toggle under “Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling” to enable the feature
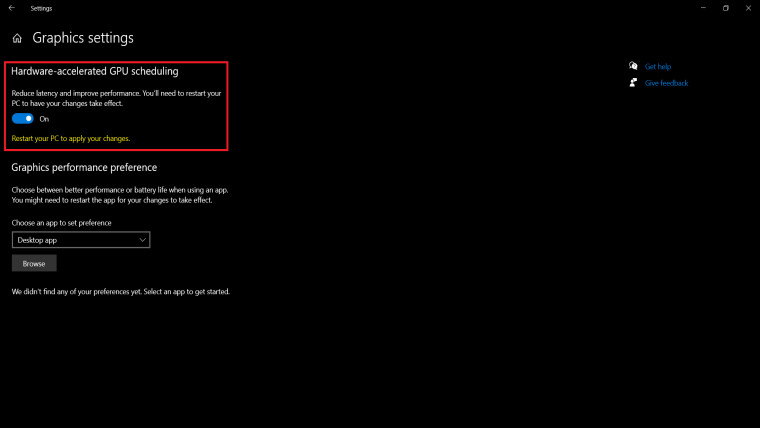
- Restart your computer to apply the changes
Do note that you will need to download and install the latest drivers for the feature to show up in Windows settings. In our tests, there was a performance boost of about 5% in games (Nvidia GeForce GTX 1660 Ti) but it depends on the GPU. Higher-tier cards with more VRAM like RTX 2080 and 2080 Ti will benefit less from the feature, while lower-tier GPUs like Nvidia’s 16 series should benefit more from hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling. AMD has also added support for hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling in the latest beta update. Selected AMD Navi based GPUs currently support the feature and you can enable it by following the aforementioned steps after downloading the latest beta drivers from AMD"s website.